In a world where data and application security is always top of mind, many solutions exist to strengthen it. One essential way is with multifactor authentication. In this post, we’ll explain what multifactor authentication (MFA) is and why it matters.
What Is Multifactor Authentication?
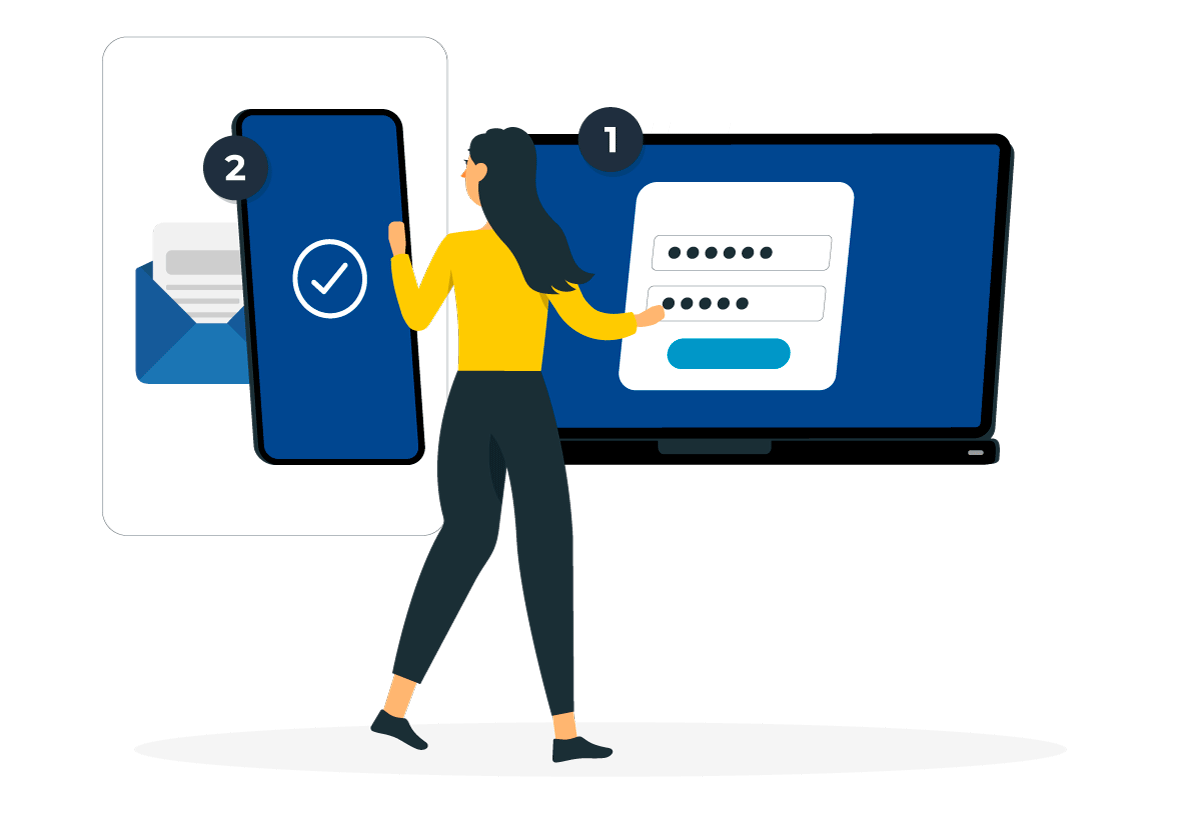
MFA is a method of authenticating a user when they log in to an account. It requires at least two verification factors to permit access. It’s a layered approach to secure data and applications. In most cases, these credentials are interdependent, such as passwords and security tokens delivered to an email address, mobile phone number or app.
MFA is a core component of a robust identity and access management (IAM) policy. Security experts highly recommend it. In a recent study, these experts considered it the most effective security control in place for protecting both on-premises and cloud-stored data.

Why Does MFA Matter?
The primary benefit of using MFA is to enhance security and permissible access. Users must verify themselves through more than just a username and password, which can be compromised. Adding MFA to any application or account fortifies its security and reduces the risk of breaches by cybercriminals. Google reported that MFA blocks 99% of bulk phishing attacks!
In addition to security, MFA supports easier user access, regardless of where employees work. As the shift to hybrid workforces continues, organizations realize that security must address all users without impacting worker access.
Another reason MFA is heavily adopted is that it’s necessary for compliance with industry regulations. For example, PCI DSS, the payment card industry data security standard, requires it.
MFA is also a critical component for companies that seek cyber insurance. It’s typically a prerequisite for an insurance company to provide coverage.
Systems can facilitate MFA in several ways, which we’ll explain next.
The Types of MFA
MFA methods fall into three categories:
- What you know (e.g., passwords, security question answers and PINs)
- Things you have (e.g., badges or smartphones)
- Biometrics (e.g., fingerprints or voice recognition)
With MFA, users will authenticate in two of these three ways. For instance, a user will log in to an account with a username and password. Then, a prompt occurs for the second verification, such as receiving a code via text message.
When you require MFA, your entire security posture improves with little additional effort on the part of your users.
What Multifactor Authentication Is: Key Takeaways
To summarize what MFA is and why it matters, here are the key takeaways:
- Increase security and reduce the risk of breaches from password-only account access.
- Mitigate the risk of poor password practices.
- Improve access to accounts and applications to boost productivity and ease of use.
- Implement MFA quickly and easily.
- Stay compliant with regulatory or other industry requirements.
Have questions about Marketron MFA practices? Visit our MFA page today.